Introduction
Hiring an employee who would be a right fit for the company has always been a challenge for the human resources department at almost every company on this planet. Traditional approaches included manually evaluating an employee after many rounds of interviews and based on feedback from interviewers, a decision was made as to whether a particular employee would be an ideal fit within the company or not. An ideal fit is defined as someone who understands the company’s vision, thrives in the work environment, and is a long-term employee. Attrition has been one major concern for these companies recently, as many employees nowadays tend to switch companies often which in turn leads to a loss of investments the company made in employee skill development.
This project aims to build a machine-learning model/s that can predict employee performance during the hiring process. The model will consider existing employees in the company and utilizing their performance over the last years, evaluate how a new employee with similar attributes will fit into the work environment at that company. This approach is unique in the sense that each person responds differently to various aspects of a work environment, and if we utilize the fact that an existing employee in that particular role has been performing well in that work environment, then it would be more accurate rather than just comparing skills or education. A major ethical issue that we will be addressing as part of this project is to look into attributes that may lead to bias and make decisions to remove any sort of bias during the hiring process.
Dataset
IBM HR Analytics Employee Attrition & Performance
This is a fictional data set created by IBM data scientists. This dataset describes 35 attributes related to 1500 employees across the company.
This dataset provides relatable attributes like Department, Education, Environment Satisfaction, and many more, that allowed us to make appropriate predictions on the performance of the employee as described in the project idea above.
Experiments
-
The dataset is split into test and training data using stratified random sampling with a division of 20% test and 80% training. The test data is utilized at a later stage to predict the accuracy of trained models.
-
Data normalization has been performed using the StandardScalar function to transform features to be on a similar scale.
-
Made use of confusion matrix to calculate precision, recall, and F1-score using Random forest, Logistic regression, Adaboost, KNN, Naive Bayes, SVM, MLP Neural Network for all three target columns, that are Attrition, Environment Satisfaction, and Job Satisfaction.
-
Compared various feature selection techniques including Select K-Best, PCA, and Lasso Regression, and selected the best technique which yields better accuracy for this particular dataset, i.e. Select K-Best.
-
The dataset is analyzed for the division of classes for target columns, and as the classes are unevenly distributed, Smote technique is being utilized to overcome this.
-
Finally, Smote, Select K-Best, and various machine learning techniques are utilized and results were analyzed to select the models to be used in Ensemble.
-
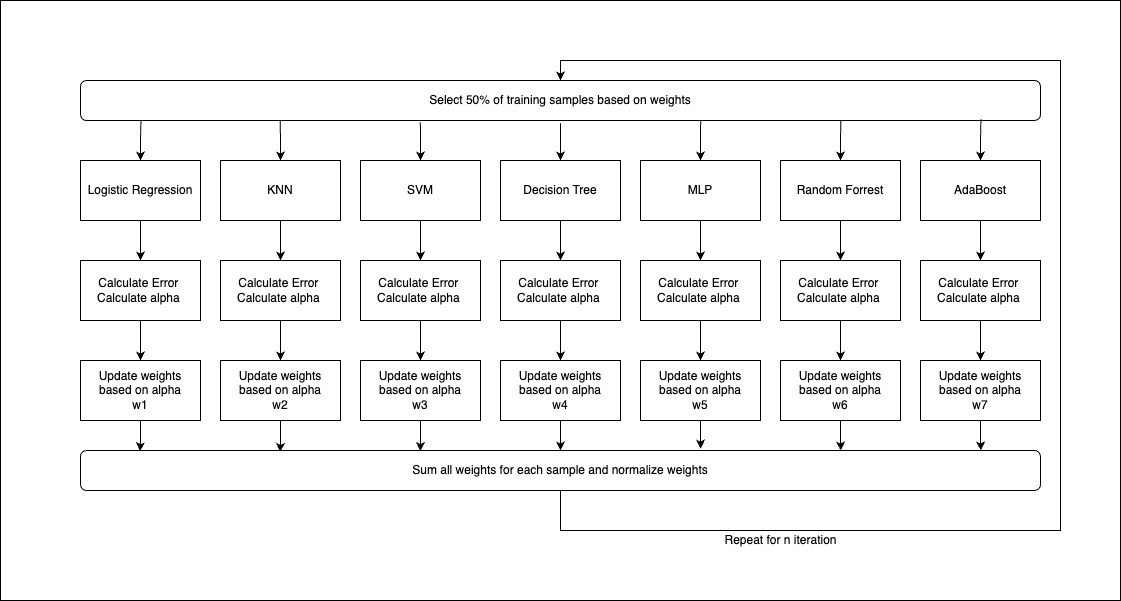
An ensemble of seven ML techniques, Random forest, Logistic regression, Adaboost, KNN, Naive Bayes, SVM, MLP Neural Network and Decision Tree are developed based on the results observed in the previous experiments. The prediction is that this would provide higher accuracy and will better fit overall data and not just the current training dataset.
-
The Ensemble implements logic similar to boosting, where in each iteration the models predict the target variable, and then the majority vote is taken, alpha and error are calculated, and the weights are reassigned for the next iteration. N such iterations are run and finally, the model is trained.
-
Clustering is applied and experiments are run to analyze if unsupervised learning benefits such a dataset or not. We consider that this will help group people with similar attributes and predict if the new employee will fit in or not. This will also help in identifying if any particular feature is acting as a bias for creating the clusters or not.
-
Both K-Means and Hierarchical clustering is implemented and results are analyzed and compared.
-
Generated graphs to compare various features and analyze if a particular feature is creating a bias against a particular section of society or not.
-
Running experiments with and without the bias columns that are Gender, Marital Status, Age, and Distance from home, and evaluating if these features generate biased outcomes or not.
-
Finally, biased features are removed and the unbiased Ensemble of models is retrained to predict if a new employee will fit in the company or not.
Outcome
-
We see that, while Environment Satisfaction and Job Satisfaction have almost equal representation of all classes, it seems like attrition has much fewer data representing class 1 as compared to class 0. Thus applying Smote technique to evenly distribute these classes would help in increasing accuracy and remove the bias toward a particular class.
-
The results of comparison of various models indicate that environment satisfaction and job satisfaction have overall low accuracy and thus aren’t that effective when predicted independently.
-
In the case of attrition, Random Forest, SVM, and KNN are the top three when considering the evaluation metrics. Thus these can be potential candidates for using these to create an Ensemble model.
-
We made an interesting observation here, we had initially considered that using the predicted values of job satisfaction and environment satisfaction as input features for attrition prediction would increase the model’s accuracy, which didn’t work in our favor. Turns out that due to the less independent accuracy of these two attributes, even when combined with attrition, they prove to be disadvantageous for attrition prediction. The tables above clearly depict this claim, we see that for all the models except for Naive Bayes, the accuracy and F1-score decreased, thus indicating that the model didn’t perform that well.
-
Utilizing seven different ML techniques to predict output and applying boosting to penalize the incorrect predictions and reward the correct ones, helped create a pretty accurate model. We got an accuracy of 0.85 and considering it’s from across seven different techniques, the chance of model overfitting to this particular dataset reduces considerably.
-
In the case of clustering, firstly 4 clusters were created based on the elbow method interpretations. We noticed that K-Means created a cluster 4 containing only the Sales department, so whenever any sales employee was predicted, there was a high chance it would automatically be assigned to cluster 4. Apart from that, the major point of the division was Age and years of experience.
-
In terms of analysis and observations, we get some pretty interesting results. We see that there is a high rate of attrition among younger people as compared to older people. We observe that current data shows that being a divorced male, there are higher chances of attrition. Finally, we observe that the following combinations {Older, Single}, {Younger, Divorced} are predicted to have a higher chance of attrition.
-
The above observations clearly show that if these features are kept in the dataset, the model will be biased towards a particular section of society and this must not be the case. There are chances that the model will not select qualifying young people only because of their age, or it might not select Divorced people because of their marital status. Thus these biases must be eliminated from the dataset and the model must be retrained.
-
We see that after removing biased features, the accuracy of the model reduces and this was expected. It is better to have a bit less accurate model than to have biased features in the model.
Conslusion
The ensemble of machine learning models with boosting was really effective and gave promising accuracy. This novel aspect of the project was inspired from Adaboost. Utilizing multiple machine learning techniques would help avoid overfitting and will work effectively on new data as well.
Identifying bias was a crucial part of this project from a ethical point of view. Whenever the decisions of model impacts human lives, bias should never be ignored. We saw how the features age, gender, marital status and distance from home had a possibility of bias against a particular section of people in society. Thus, we removed these features, even though it meant a reduction in accuracy of our models.
Repository https://github.com/deep-mm/Potential-Performance-Predictor
Research: Potential_Performance_Predictor.pdf
Technology: Python, Jupyter-Notebook
ML Techniques: Ensemble, Adaboost, Clustering, Feature-Selection, Logistic-Regression, KNN, SVM, Decision-Tree, MLP, Random-Forest